Female Subfertility Diseases
Index
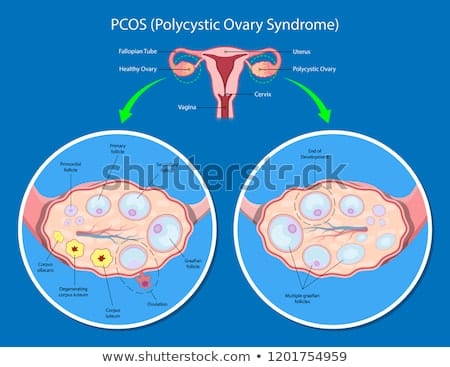
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Introduction
PCOS is caused by female reproductive hormonal imbalance. This hinders the proper release of eggs from ovules and affects ovulation.
Causes
Exact causes of PCOS is unknown. But experts assume a few reasons such as
- Heredity – It is suggested that certain genes may cause PCOS.
- Excess Androgens – Although these are called “male hormone”, it is present in both male and females.
- Low-grade inflammation – Inflammation is the process of fighting against infections. The body produces inflammatory factors called ‘cytokines’. PCOS have a type of low-grade inflammation that stimulates polycystic ovaries to produce androgens, which can lead to heart and blood vessel problems.
- High level of insulin – High levels of insulin. Insulin is a hormone that controls how the food you eat is changed into energy. Excess insulin might increase androgen production, causing difficulty with ovulation.
Symptoms

- Irregular periods – Infrequent, irregular or prolonged periods.
- Excess androgen – Increased levels of the male hormone may result in physical signs, such as Too much hair, acne, thinning hair, weight gain, darkening of the skin, skin tags.
- Polycystic ovaries – Your ovaries might be enlarged and contain follicles that surround the eggs. As a result, the ovaries might fail to function regularly.
Hypothalamic dysfunction (Hypothalamic Amenorrhea)
Introduction
Hypothalamus in the brain is responsible for producing hormones that control production and the release of eggs. Dysfunction on producing such hormones would stop mensuration (monthly period) and therefore cause infertility.
Causes
- Birth defects of the brain or hypothalamus
- Genetic disorders
- Eating disorders
- Tumours
- Head trauma
- Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections
- Autoimmune disorders (Disorders that cause abnormalities in the immune system)
- Malnutrition
- Cranial radiation – (By Cancer treatments)
- Too much iron
Symptoms
Missing periods for prolonged periods and light bleeding during menstruation are the most apparent symptoms. Others may include
- Low sexual desire (Libido)
- Feeling cold regularly
- Depression and anxiety
- Sleeping difficulty
- Increased hunger
- Low energy
Premature ovarian failure
Introduction
Your ovaries usually stop producing eggs after the age of 40. Premature ovarian failure is a condition where your ovaries stop producing normal amounts of hormones to produce eggs before 40. This is different from menopause where ovulation stops completely.
Causes
- Genetic Disorders
- Toxins – Chemotherapy and radiation can damage cells.
- Autoimmune disease – A condition which the body damages its own tissues mistakenly. (Read more)
Symptoms
Common symptoms for this failure are similar to that of estrogen deficiency and menopause.
- Irregular periods
- Difficulty in conceiving
- Hot flashes (Sudden feeling of warmth in your upper body)
- Nightly sweats
- Dry Vagina
- Decreased Libido (Sexual desire)
Hyperprolactinemia
Introduction
This condition causes your pituitary gland to produce excessive amounts of prolactin hormone. Prolactin triggers milk production in women. It exists in a little amount in every woman but excessive amounts can cause irregular or no ovulation.
Causes
- A Benign tumour growing in the pituitary gland
- Limited production of thyroid hormone (hypothyroidism)
- Certain medications
Symptoms
- Irregular periods
- Produce milk when not pregnant (Galactorrhea)
Pelvic inflammatory disease

Introduction
Pelvic inflammatory is an infection within the female reproductive system usually caused by sexually transmitted bacterias transferring to your fallopian tubes, uterus and ovaries.
Causes
The main culprits are sexually transmitted diseases such as chlamydia and gonorrhoea. But other non sexually transmitted infections can also cause this condition.
Symptoms
PID might not show signs immediately in mild cases and tests should be done to detect the disorder. However, following the symptoms may indications of prevalent pelvic inflammation.
- Pain in your lower abdomen (Pelvis)
- Fever with chills
- An unusual discharge with a bad smell from your vagina
- Pain and/or bleeding when you’re having sex
- Burning sensation when you urinate
- Bleeding between periods
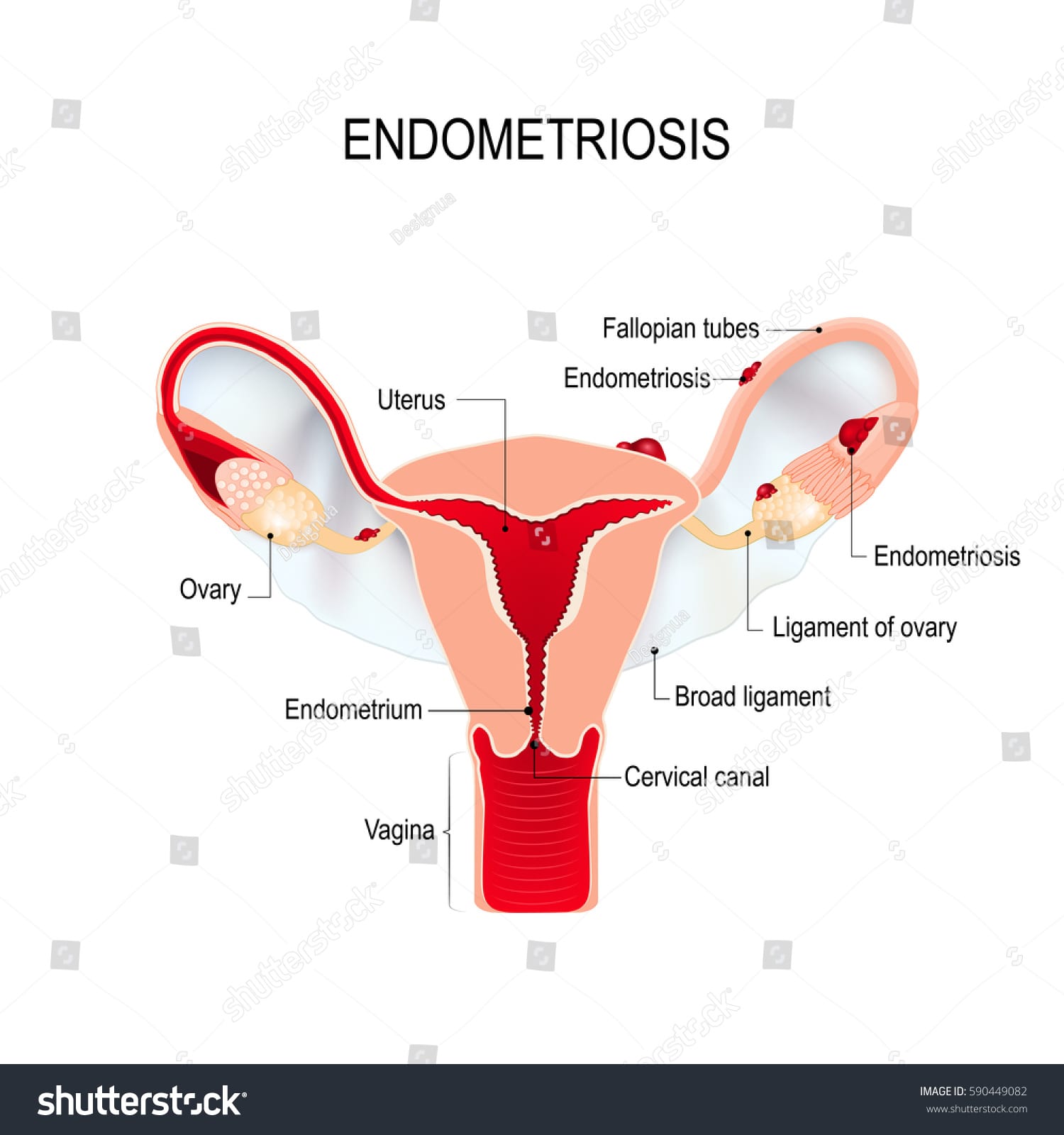
Endometriosis
Introduction
Endometriosis is a common cause of subfertility where tissues that are supposed to be lined inside of uterus grows in other parts of the reproductive system such as fallopian tubes and ovaries hindering proper ovulation and conception.
Causes
Exact causes of endometriosis are not deducted but possibilities are as follows.
- Retrograde menstruation – Happens when tissues and blood from uterus flow back to the fallopian tube instead of out of the body.
Cell transformations - Immune system disorders
Symptoms
The most significant sign is severe pain in the pelvic area (The area between your vagina and stomach). The pain can happen in the period or when having sex. Other symptoms to look out for,
- Pain with bowel movement
- Bloating
- Blood in the urine or painful urination
- Abnormal bleeding from the vagina
- Constipation
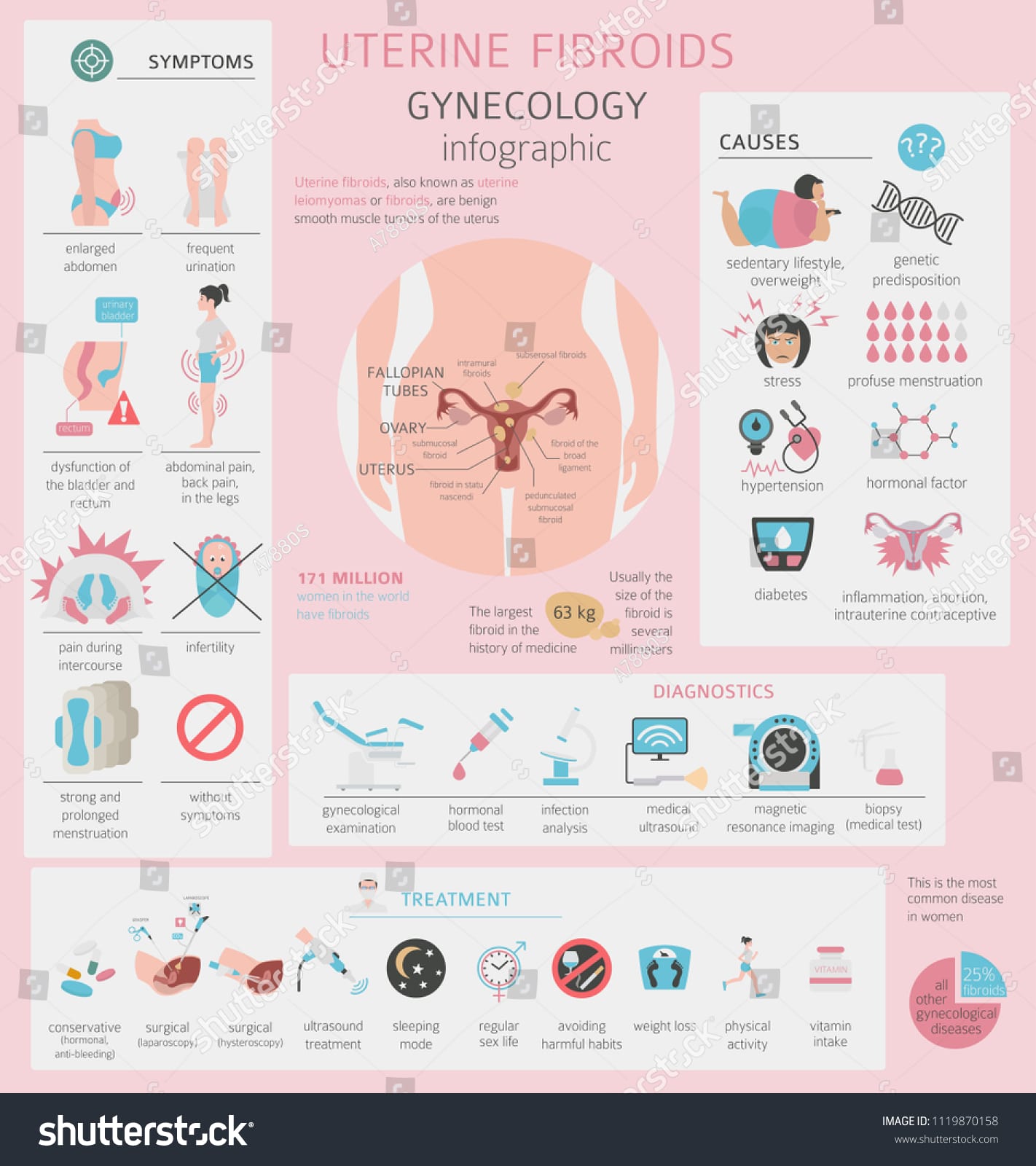
Uterine Fibroids
Introduction
Uterine fibroids also called myomas, leiomyomas, or fibromas are benign tumours that grow inside the uterus of women in the fertile age. These don’t cause cancer nor detectable in most situations. In severe cases, these can distort the uterus and hinder the conception.
Causes
Exact reasons are not yet deduced but researches have emphasized the following contributing factors.
- Diverging muscle cells in uterus develop into fibroids with the influence of estrogen.
- Hormones such as Estrogen and Progesterone can cause the growth of fibroids.
- Heredity
- Lifestyle factors such as birth control, Vitamin D deficiency, alcohol, low organic food and dairy intake.
Symptoms
Symptoms may not be apparent depending on the size of the fibroids. Following are considered the most common symptoms.
- Heavy and prolonged periods
- Unusual bleeding when having a period
- Pain in the pelvic area
- Pain during sex
- Pain in the lower back or legs
- Frequent urination
- An apparent muscle mass located in the pelvis area
- Constipation or difficulty in emptying the bladder
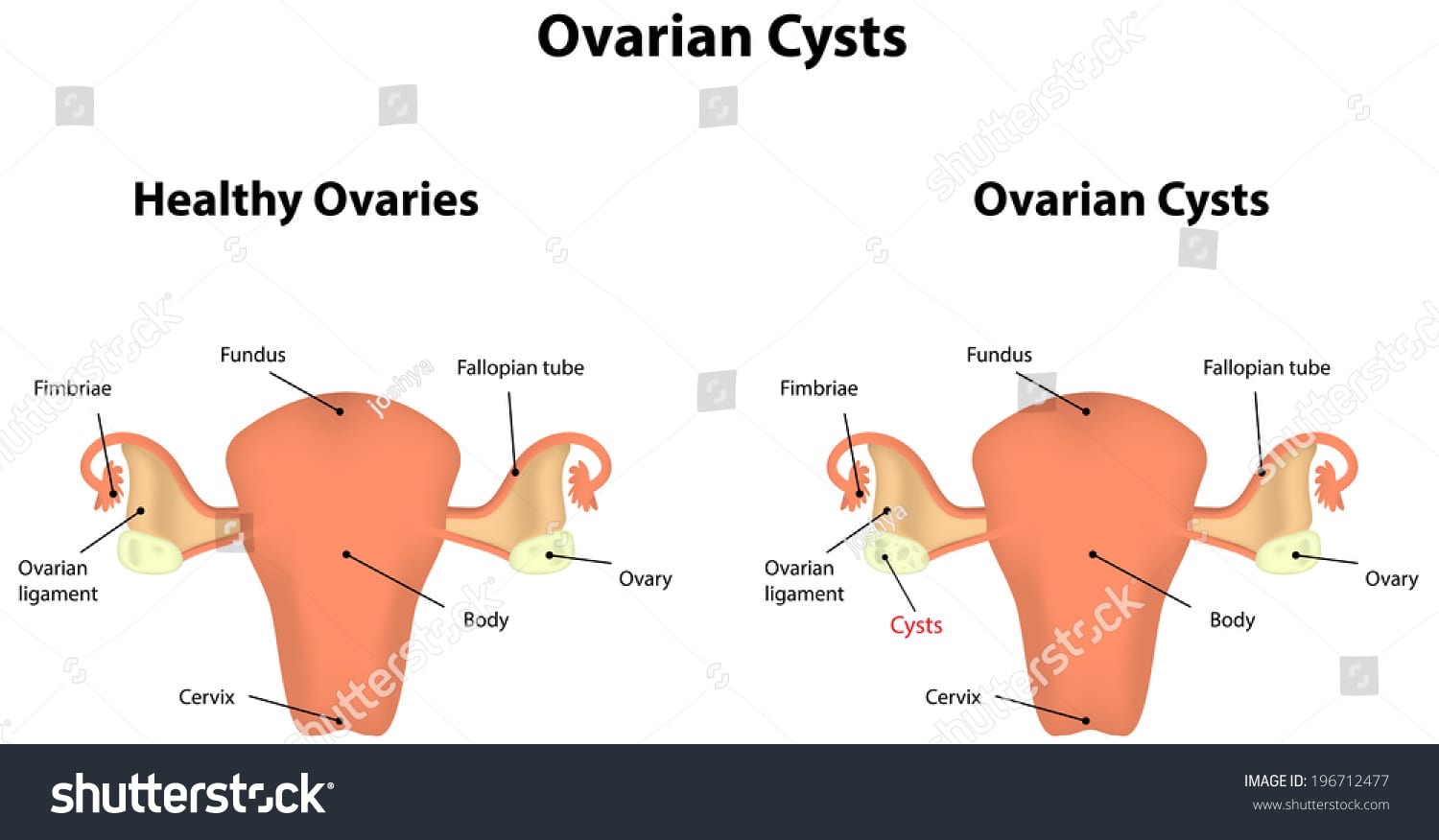
Ovarian cysts
Introduction
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacks that develop on or within ovaries. These are usually benign but can cause severe harm if ruptured. These usually don’t cause subfertility but make it difficult to get pregnant.
Causes
Most probable causes of cysts are as follows.
- Endometriosis – Tissues from uterus can grow upon ovaries.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Follicular Cysts
- Corpus luteum cysts
- Dermoid cysts
- Cystadenomas
- Endometriomas
Symptoms
Benign cysts cause no trouble and pain. A large or ruptured cyst may show the following symptoms. It might even block the blood supply to ovaries.
- Pain in the pelvic area – An ache on the side where the cyst is
- Bloating or constipation
- Frequent need to urination
- Heavy or irregular periods
- Feeling bloated even after a small food intake
- The difficulty of getting conceived